Kenali Perbedaan MCB, ACB, MCCB
The article is written by ElectGo team with contributions from Mr. Colin Koh, an industrial educator and industry leader in smart manufacturing and automation.
Pengertian ACB, MCB, MCCB
Pemutus arus listrik (circuit breaker) merupakan komponen penting untuk melindungi rangkaian listrik dari kerusakan akibat arus lebih atau hubungan pendek. Tiga jenis utama yang sering digunakan adalah ACB (Air Circuit Breaker), MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker), dan MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker). Masing-masing memiliki karakteristik dan fungsi yang berbeda.


ACB (Air Circuit Breaker)
Air Circuit Breaker (ACB) adalah pemutus sirkuit listrik yang menggunakan udara sebagai media pemadam busur listrik (arc) saat memutus arus. Biasanya digunakan untuk sistem distribusi daya tinggi dan perlindungan arus besar pada aplikasi industri besar.


MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)
Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) adalah pemutus sirkuit kecil yang berfungsi untuk melindungi sirkuit listrik bertegangan rendah dari arus berlebih dan korsleting. MCB biasanya digunakan dalam aplikasi rumah tangga atau beban kecil.


MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker)
Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB) adalah pemutus sirkuit listrik yang memiliki casing cetakan (molded case) dengan kemampuan proteksi untuk arus menengah hingga tinggi. Digunakan dalam aplikasi industri, komersial, dan perlindungan arus besar dengan fitur proteksi lebih fleksibel dibanding MCB.
Perbedaan secara spesifikasi
| Kriteria | ACB | MCB | MCCB |
| Kapasitas Arus | 630 A hingga 6300 A | Hingga 125 A | 16 A hingga 1600 A |
| Tegangan Operasi | 380 V – 6600 V | 220 V – 440 V | 220 V – 690 V |
| Media Pemutus | Menggunakan udara sebagai media pemutus | Sistem thermal-magnetik | Sistem thermal-magnetik atau elektronik |
| Kemampuan Pemutusan | Sangat tinggi (hingga 100 kA) | Rendah (hingga 10 kA) | Menengah-tinggi (hingga 50 kA) |
| Fitur Tambahan | Bisa diprogram, dengan proteksi overload dan earth fault | Tidak bisa diprogram | Bisa memiliki proteksi tambahan seperti overcurrent dan short circuit |
- ACB (Air Circuit Breaker) adalah pilihan yang tepat jika Anda membutuhkan perlindungan untuk arus besar di atas 630 A. ACB biasanya digunakan di sistem distribusi daya utama, seperti pembangkit listrik, pabrik besar, atau gedung komersial utama. Alat ini cocok untuk aplikasi tegangan menengah hingga tinggi, serta dilengkapi fitur proteksi canggih seperti Earth Fault, Overload, dan pemrograman arus lepas (trip). ACB juga ideal jika Anda memerlukan kemampuan pemadaman busur listrik yang tinggi dan pengaturan fleksibel.
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) lebih cocok untuk perlindungan beban kecil, seperti instalasi rumah tangga atau kantor kecil dengan arus maksimum hingga 125 A. Alat ini dirancang untuk melindungi sirkuit dari arus berlebih atau korsleting kecil. MCB biasanya digunakan di panel listrik rumah, pencahayaan, atau peralatan kecil karena ukurannya yang kompak, ekonomis, dan mudah dipasang. Pilih MCB jika kebutuhan Anda sederhana dan tidak memerlukan pengaturan yang kompleks.
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) adalah solusi ideal untuk aplikasi dengan arus menengah hingga tinggi (16 A hingga 1600 A). MCCB sering digunakan di gedung komersial, pabrik, atau aplikasi industri yang membutuhkan perlindungan lebih fleksibel dibandingkan MCB. MCCB dapat digunakan untuk melindungi beban listrik menengah hingga besar dengan kemampuan tambahan seperti Overload, Short Circuit, dan proteksi Ground Fault. Pilih MCCB jika Anda memerlukan proteksi yang lebih kuat dari MCB tetapi tidak membutuhkan kapasitas sebesar ACB.
Untuk memilih yang tepat, pastikan Anda mempertimbangkan kapasitas arus, tegangan operasi, lingkungan aplikasi, serta kebutuhan fitur proteksi tambahan. Jika ragu, selalu sesuaikan dengan spesifikasi dan standar instalasi yang berlaku.
Temukan Produk Circuit Breaker
What is the common Punchout catalog process?
There are 6 common steps of the Punchout catalog.
Please note that the punchout process may vary slightly depending on the level of punchout integration.
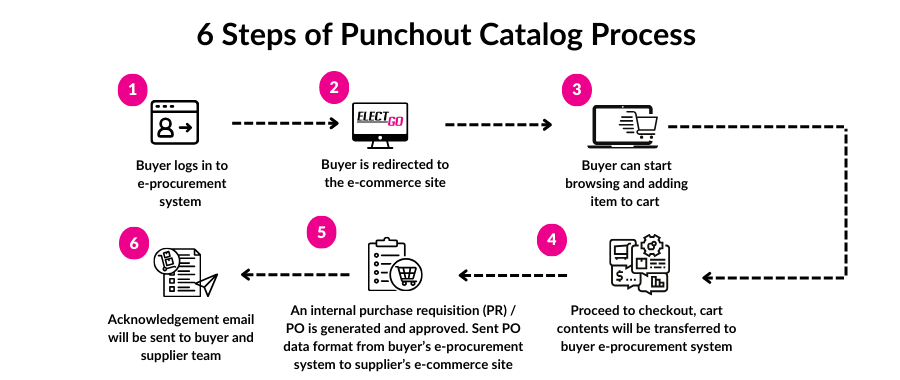

Step 1: Buyer logs into e-procurement system
The process begins with the buyer logging into their e-procurement system. This is where they manage and initiate procurement activities.
Step 2: The buyer is redirected to the supplier’s e-commerce site
From the e-procurement system, the buyer is seamlessly redirected to the supplier’s e-commerce site. This integration allows for a smooth transition without the need for separate login credentials.
Step 3: Buyer starts browsing and adding items to the cart
Once on the supplier’s e-commerce site, the buyer can browse the catalog, view product details, and add desired items to their shopping cart. This stage involves selecting products that meet their procurement needs.
Step 4: Proceed to checkout, cart contents are transferred to the buyer's e-procurement system
After finalizing the selection of items, the buyer proceeds to the checkout. At this point, the contents of the shopping cart are transferred back to the buyer's e-procurement system.
Step 5: Internal Purchase Requisition (PR) / Purchase Order (PO) generated and approved
Within the e-procurement system, an internal Purchase Requisition (PR) or Purchase Order (PO) is generated based on the cart contents. This PR/PO is then subject to the organization's approval workflow, ensuring that the procurement complies with internal policies and budget constraints. Once approved, the PO data is sent in the appropriate format from the buyer's e-procurement system to the supplier’s e-commerce site.
Step 6: Acknowledgement email sent to buyer and supplier team
Finally, an acknowledgment email is sent to both the buyer and the supplier team, confirming the receipt and processing of the order. This communication ensures that all parties are informed about the status of the procurement, facilitating transparency and coordination
Benefits of Punchout catalog for both buyers and suppliers
Benefits for buyers
![]()
Seamless procurement process
- Simplify the purchasing process by integrating directly with the buyer's e-procurement system.
- Reduce manual work and human error.
![]()
Real-time access to supplier data
- Access real-time data from suppliers, including up-to-date pricing and product availability.
- Improve the decision-making.
![]()
Compliance and control
- Adhere to internal procurement policies by restricting purchases to pre-approved suppliers, contracted pricing, and specific products.
- Ensure orders go through the proper channels for authorization before being processed.
![]()
Cost and time savings
- Time-saving by reducing the procurement process including placing and approving orders.
- Cost efficiency by reducing errors and adjustments.
![]()
Enhanced supplier relationships
- Provide buyers with direct access to trusted suppliers
- Buyers can access a tailored catalog that only includes contract-specific products and prices.
Benefits for suppliers
![]()
Increased business from larger buyer
Access to enterprise clients who rely on e-procurement systems like SAP, Oracle, or Coupa. By making procurement easier and more efficient helps to increase a loyal customer base.
![]()
Improved order accuracy
Automated data transfer helps reduce the chance of discrepancies or disputes between the supplier and buyer.
![]()
Faster order processing
Streamline order flow helps to ensure that orders are processed quickly and efficiently. It also helps to reduce administrative works.
![]()
Improved inventory management
With more accurate demand forecasting from real-time data, suppliers can better manage their inventory and supply chain, improving overall operational efficiency.
![]()
Increased customer satisfaction
Offer buyers a customized catalog that reflects negotiated prices, preferred products, and relevant promotions, ensuring a positive and personalized buying experience.
By providing real-time data can help to build trust from buyers.
What are the common challenges of the Punchout catalog?
Implementing a Punchout catalog can significantly streamline the procurement process for organizations, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some common challenges faced when implementing a Punchout catalog:
1. Integration complexity: Integrating Punchout catalogs with existing e-procurement systems can be technically complex. Organizations may face challenges in ensuring compatibility between different systems, which can lead to delays in implementation and require significant IT resources.
2. Supplier readiness: Not all suppliers may be equipped to support Punchout catalogs. Some suppliers may lack the necessary technology or expertise to create and maintain a Punchout catalog, which can limit the selection of suppliers available for Punchout integration.
3. User training and adoption: Employees may require training to effectively use the Punchout catalog. Resistance to change or a lack of familiarity with the new system can hinder adoption. Organizations need to invest in user training and support to facilitate a smooth transition.
4. Cost considerations: While Punchout catalogs can lead to cost savings in the long run, the initial setup and integration costs can be significant. SMEs may find it challenging to justify these costs, especially if the expected return on investment is not clearly defined.
By proactively planning for these challenges, organizations can maximize the advantages of Punchout catalogs and enhance their overall procurement efficiency.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The main purpose of a Punchout catalog is to enable seamless and efficient procurement. With Punchout, purchasing teams can browse, select, and order products from a supplier without leaving their internal procurement software. The Punchout solution automatically updates product availability, pricing, and other relevant information, eliminating manual entry and reducing errors.
A Punchout catalog requires the following technical elements:
- Procurement system compatibility: The supplier's Punchout catalog must integrate with the buyer’s procurement system, such as SAP, Ariba, Oracle, or Coupa.
- Supported protocols: Punchout typically uses cXML (for Ariba and SAP systems) or OCI (for SAP systems).
- Secure access: Ensure that authentication methods like SSO or token-based authentication are set up to secure access for buyers.
- Real-time data integration: The catalog should provide real-time updates on product availability, pricing, and stock levels.
- Customization: The ability to tailor the catalog interface, pricing, and content to suit the buyer’s needs and requirements.
The buyer and supplier must work together to create a catalog that meets the buyer's purchasing needs. The supplier builds and hosts this catalog on their e-commerce website, designed specifically for integration with the buyer’s procurement platform.
Here's how the buyer and supplier collaborate:
- Requirement gathering: The buyer outlines their specific procurement requirements, including product categories, pricing structures, and any contract terms that need to be reflected in the Punchout catalog. The supplier needs to understand the buyer's preferences and procurement policies to build a suitable catalog.
- Catalog customization: The supplier builds a customized catalog on their e-commerce website. This catalog is specifically designed for Punchout, showing only the products, pricing, and availability negotiated in the buyer’s contract. The supplier ensures that the catalog can integrate with the buyer's procurement system through a compatible Punchout protocol (like cXML or OCI).
- Testing and integration: Both the buyer and supplier test the Punchout integration to ensure that when the buyer "punches out," they can browse, select, and transfer items to their internal procurement system seamlessly.



































Share this article on social media