Masalah Umum pada Circuit Breaker dan Cara Mengatasinya
Semua perangkat dan peralatan listrik, mulai dari sistem pencahayaan hingga HVAC dan sistem bangunan pintar, bergantung pada circuit breaker. circuit breaker yang berfungsi dengan baik adalah kunci kelancaran operasional bangunan komersial Anda. Inspeksi kelistrikan rutin dapat mendeteksi masalah sebelum menjadi lebih serius. Namun, kerusakan pada pemutus arus tetap mungkin terjadi dan seringkali memerlukan penggantian. Bagaimana cara mengenali tanda-tanda kerusakan pada circuit breaker?
1. Beban Listrik Berlebihan (Circuit Overload):
- Penyebab: Kelebihan beban atau Circuit Overload, yang merupakan penyebab paling umum dari trip pemutus arus listrik, terjadi ketika perangkat yang terhubung ke rangkaian listrik membutuhkan arus listrik yang lebih besar daripada yang dapat disuplai oleh rangkaian tersebut. Misalnya, menggunakan breaker 10 Ampere untuk perangkat yang membutuhkan lebih dari itu.
- Solusi: untuk mengatasi kelebihan beban adalah dengan mendistribusikan beban secara lebih merata dengan menghubungkan beberapa perangkat ke rangkaian listrik lainnya.
2. Korsleting (Short Circuit):
- Penyebab: Korsleting atau Short Circuit terjadi ketika bagian yang terisolasi dari kabel "hidup" (hitam) secara fisik bersentuhan dengan kabel hitam lainnya atau kabel netral putih. Hal ini menyebabkan lonjakan arus listrik ke dalam rangkaian yang menyebabkan pemutus arus listrik langsung trip.
Korsleting dapat terjadi ketika kabel mengalami degradasi akibat usia dan isolasi terkelupas atau retak, sehingga memungkinkan kabel terbuka bersentuhan. Atau dapat disebabkan oleh kerusakan internal pada perangkat apa pun yang terhubung ke stopkontak pada rangkaian tersebut. - Solusi: Korsleting harus dilacak ke sumbernya dengan mencari stopkontak yang berubah warna, kabel listrik yang meleleh atau retak, atau perangkat apa pun yang mengalami malfungsi atau mengeluarkan bau kabel terbakar. Jika penyebab eksternal yang jelas tidak dapat segera diidentifikasi, kemungkinan masalahnya terletak pada kabel listrik itu sendiri. Matikan sakelar pemutus arus listrik dan hubungi teknisi listrik profesional untuk melacak masalahnya.
3. Arus Tanah (Ground Fault)
- Penyebab: Arus tanah atau Ground Fault terjadi ketika kabel hidup dalam rangkaian bersentuhan dengan kabel grounding atau komponen logam yang di-grounding seperti kotak stopkontak logam. Arus tanah hanyalah versi lain dari korsleting yang menyebabkan kelebihan beban listrik yang memicu pemutus arus listrik untuk trip sebagai responsnya.
- Solusi: Menemukan dan memperbaiki arus tanah dapat dilakukan oleh teknisi listrik yang berkualifikasi dengan menggunakan peralatan yang dirancang khusus untuk memecahkan masalah rangkaian listrik.
4. Bau Terbakar/Stopkontak Panas/ Sengatan Listrik
- Kedip-kedip Lampu: Ketika lampu Anda berkedip-kedip atau redup, itu bisa mengindikasikan adanya masalah dengan pemutus arus listrik Anda. Namun, banyak orang tidak yakin apakah tanda spesifik ini berarti ada masalah dengan perlengkapan lampu atau pemutus arus listrik. Cara sederhana untuk mengidentifikasinya adalah dengan memperhatikan saat lampu berkedip-kedip. Misalnya, jika Anda menyalakan peralatan bertegangan tinggi seperti pemanas ruangan atau AC, maka Anda mungkin melihat lampu meredup. Ini menunjukkan bahwa masalahnya terletak pada pemutus arus listrik. Untuk mengatasi masalah ini, Anda dapat memasang rangkaian alternatif untuk peralatan bertegangan tinggi.
- Berbau: Jika Anda mencium bau plastik terbakar, belerang, atau bau telur busuk, tanpa sumber yang dapat diidentifikasi, maka masalahnya mungkin terletak pada pemutus arus listrik Anda. Penting untuk menghubungi tukang listrik segera setelah Anda mencium bau aneh karena ini menunjukkan pemutus arus listrik rusak. Memperbaikinya sesegera mungkin akan melindungi ruang Anda dari risiko kebakaran potensial.
- Stopkontak Panas: Kita sering berpikir bahwa wajar jika peralatan atau stopkontak sedikit hangat saat digunakan. Sebaliknya, pemanasan stopkontak dan pelat sakelar ini merupakan tanda bahwa ada yang salah dengan pemutus arus listrik. Jika Anda pada suatu waktu melihat pemanasan sistem kelistrikan Anda, maka matikan aliran listrik dan segera hubungi tukang listrik. Stopkontak yang panas tidak boleh dibiarkan tanpa pengawasan dalam waktu lama.
- Sengatan Listrik: Jika Anda merasakan percikan dan sengatan listrik saat menyentuh peralatan atau papan sirkuit Anda, maka ini menunjukkan adanya masalah pada papan sirkuit. Misalnya, jika Anda merasakan kesemutan saat menyalakan atau mematikan lampu atau sakelar lainnya, maka segera matikan pasokan listrik. Sengatan listrik dan percikan seperti itu dapat meningkat menjadi kebakaran listrik jika tidak segera ditangani.
- Suara Dengung: Jika Anda mendengar suara dengung dari pemutus arus listrik Anda, maka ini menunjukkan adanya kelebihan beban. Dalam situasi seperti ini, pemutus arus listrik tidak dapat mati dengan sukses dan ini dapat menyebabkan percikan api. Dalam situasi seperti ini, sebaiknya hubungi tukang listrik dan jangan menggunakan peralatan atau perangkat apa pun.
Menjaga circuit breaker dalam kondisi baik dan memastikan instalasi listrik yang tepat sangat penting untuk keselamatan dan efisiensi sistem kelistrikan Anda. Jika Anda mengalami masalah yang tidak dapat diatasi sendiri, sebaiknya hubungi profesional di bidang kelistrikan.
Untuk mereset circuit breaker, matikan sakelarnya ke posisi 'off'. Kemudian, hidupkan kembali. Berdirilah sedikit menjauh dari panel saat melakukannya, untuk berjaga-jaga jika terjadi percikan api. Sebagai tindakan pencegahan, Anda bisa mengenakan kacamata pelindung.
Siapkan diri Anda untuk kemungkinan pemadaman listrik. Sediakan senter dan baterai di dekat panel listrik untuk penerangan jika listrik padam (dan jika Anda tidak dapat menggunakan senter di ponsel Anda untuk menghemat baterai). Tunggu beberapa menit setelah mereset pemutus arus listrik sebelum mencolokkan kembali peralatan Anda untuk mengetahui apa yang menyebabkan kelebihan beban pada rangkaian


Sourcing
Enable organizations to identify, evaluate, and select suppliers electronically. Tools like e-tendering and online auctions are used to solicit and compare bids from multiple suppliers, ensuring competitive pricing and terms.


Purchase requisition and approval
Employees can submit online purchase requests routed through a predefined approval workflow. This streamlines the approval process, reduces manual errors, and ensures all purchases align with the organization’s procurement policies.

Order management
Automate the creating, submitting, and tracking of purchase orders (POs). This includes automatic PO generation, order confirmation, and delivery tracking, which enhances order accuracy and fulfillment efficiency.


Supplier management
Facilitate better supplier relationships by providing tools for supplier evaluation, performance monitoring, and collaboration. Supplier portals allow for easy communication and information exchange, improving overall supplier management.


Contract management
E-procurement includes tools for managing contracts electronically, from creation and negotiation to execution and renewal. This function ensures contractual terms and conditions compliance, reduces risks and improves contract lifecycle management.


Invoicing and payment
The system automates the processing of invoices, matching them with purchase orders and delivery receipts to ensure accuracy before payment. This reduces the risk of errors, prevents fraudulent activities, and accelerates the payment process.

Reporting and analytics
Provide advanced reporting and analytics tools, offering insights into spending patterns, and supplier performance. These insights help organizations make informed decisions, identify cost-saving opportunities, and optimize their procurement strategies.
3. What is the e-procurement process?
The e-procurement process typically follows these key stages:
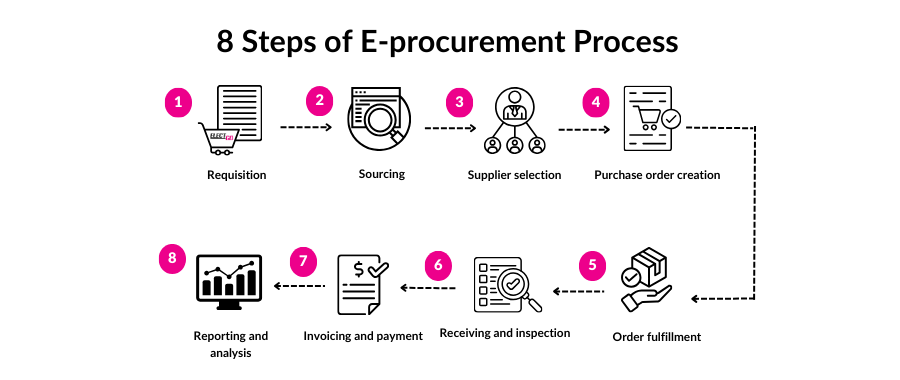
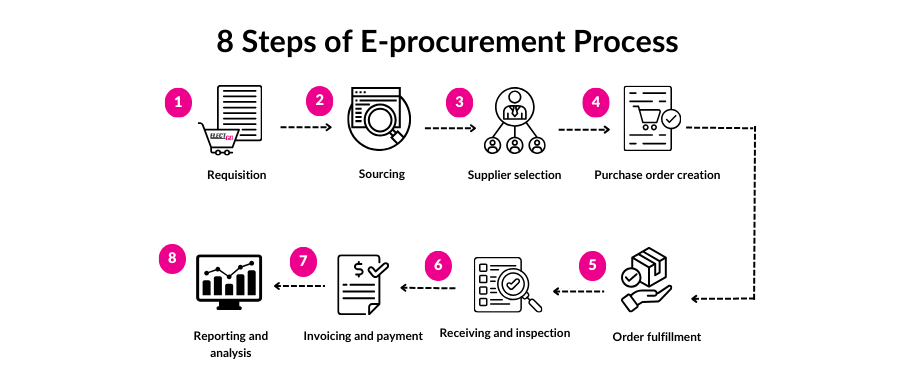
3.1 Requisition
The process begins with the submission of a purchase requisition by a department or employee, which outlines the required goods or services. The e-procurement system routes this requisition through an automated approval workflow based on pre-established rules.
3.2 Sourcing
Once the requisition is approved, the e-procurement system facilitates the sourcing process. This may involve sending out requests for proposals (RFPs) or quotes (RFQs) to prequalified suppliers, hosting online auctions, or accessing digital catalogs to find the best suppliers.
3.3 Supplier selection
Suppliers submit their bids or quotes electronically, which are then evaluated by the procurement team. The e-procurement system helps compare bids based on criteria such as price, delivery time, quality, and compliance with specifications. The selected supplier is then notified electronically.
3.4 Purchase order creation
After the supplier is chosen, the e-procurement system automatically generates a purchase order (PO) based on the requisition and supplier information. This PO is sent to the supplier electronically, confirming the order details.
3.5 Order fulfillment
The supplier fulfills the order by delivering the goods or services as specified. The e-procurement system tracks the order status, ensuring timely delivery and notifying the buyer of any delays or issues.
3.6 Receiving and inspection
Upon receiving the goods or services, the buyer inspects them to ensure they meet the specified requirements. The e-procurement system records the receipt and any discrepancies, if any, in the delivery.
3.7 Invoicing and payment
The supplier submits an electronic invoice, which is matched with the purchase order and receipt in the e-procurement system. Once verified, the payment is processed automatically, completing the transaction.
3.8 Reporting and analysis
The e-procurement system captures data throughout the process, generating reports and analytics to provide insights into procurement activities. This data can be used to evaluate supplier performance, identify savings opportunities, and improve future procurement strategies.
4. What are the benefits and drawbacks of e-procurement?
4.1 Benefits of e-procurement
- Increased efficiency: By automating routine tasks such as order processing, approval workflows, and invoicing, eProcurement reduces the time and effort required to complete procurement activities, allowing procurement professionals to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Cost savings: Achieve better pricing through competitive bidding, bulk purchasing, and improved supplier negotiations. It also reduces administrative costs by minimizing manual processes and errors.
- Enhanced transparency: Provide real-time visibility into procurement activities, ensuring compliance with procurement policies and reducing the risk of fraud. Audit trails and reporting features also enhance transparency and accountability.
- Better supplier management: Improve supplier relationships by providing tools for performance monitoring, communication, and collaboration. Suppliers benefit from streamlined processes, faster payments, and increased business opportunities.
- Improved compliance: Ensures that all procurement activities adhere to organizational policies and regulatory requirements. Automated approval workflows and contract management tools help enforce compliance and reduce risks.
- Data-driven decision-making: Provide valuable insights into procurement activities through advanced reporting and analytics tools. Organizations can use this data to optimize procurement strategies, identify cost-saving opportunities, and improve supplier performance.
4.2 Drawbacks of e-procurement
- Implementation costs: Can be expensive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Costs may include software licensing, customization, training, and integration with existing systems.
- Complexity: Can be complex to implement and operate, requiring significant changes to existing procurement processes. Organizations may need training and change management to ensure successful adoption.
- Dependence on technology: E-procurement system relies heavily on technology, making it vulnerable to system downtime, cybersecurity threats, and data breaches. Organizations must ensure their eProcurement systems are secure, reliable, and regularly updated.
- Resistance to change: Employees and suppliers may only accept transitioning from traditional procurement methods to e-procurement, especially if unfamiliar with the new technology. This resistance can hinder the system’s successful adoption.
5. What are the differences between e-procurement and procurement
| Factor | E-procurement | Procurement |
| Sourcing and acquiring goods/services | Digitally enhances this process by integrating technology to streamline and automate the procurement activities. | Involves sourcing, negotiating, and acquiring goods, services, or works from external suppliers. |
| Supplier management | Digitizes supplier management tasks such as supplier bidding and selection through automated systems. | Includes activities like supplier selection and contract management. |
| Order processing | Automates order processing tasks like purchase requisitions and invoice processing, reducing manual effort and errors. | Involves order processing, which is typically done manually or through paper-based methods. |
| Efficiency and transparency | Enhances efficiency, transparency, and data-driven decision-making by leveraging digital tools and real-time insights. | Aimed at managing the procurement process, though it may be time-consuming and prone to errors due to manual processes. |
Want to know more about procurem
- Credit term solution provides a mechanism for managing financial transactions between buyers and suppliers, offering flexibility in payment and improving cash flow. It also enhances procurement efficiency and financial management, making them a valuable component of a comprehensive eProcurement strategy
- Punchout solution is a digital catalogs that allow buyers to browse and purchase goods and services from pre-approved suppliers. eCatalogs streamline the purchasing process, ensuring compliance with procurement policies and reducing maverick spending.
- Supplier portals: Online platforms that facilitate communication and collaboration between buyers and suppliers. Supplier portals provide a centralized hub for managing interactions, streamlining procurement processes, and exchanging information. Through these portals, suppliers can submit bids, manage orders, track payment status, and access important documents and updates. Buyers, in turn, can review supplier performance, manage contracts, and ensure compliance with procurement policies.


Share this article on social media