Pengertian Timer: Time Delay Relay, Timer Analog, dan Timer Digital
Apa itu Timer
Timer adalah perangkat kontrol yang mengeluarkan sinyal pada waktu yang telah ditentukan setelah menerima sinyal input. Timer digunakan untuk mengukur interval waktu tertentu. Namun, dalam istilah teknik elektro, timer juga sering disebut sebagai counter. Timer adalah komponen yang banyak digunakan dalam berbagai sistem embedded. Mereka digunakan untuk mencatat waktu untuk berbagai kejadian yang terjadi dalam sistem embedded.
Nilai timer secara otomatis diatur ulang menjadi nol setelah mencapai nilai maksimumnya. Setelah nilai maksimum untuk timer tercapai, interupsi dihasilkan dengan bendera overflow. Timer dapat digunakan untuk mengukur waktu yang telah berlalu atau kejadian eksternal yang terjadi untuk interval waktu tertentu. Mereka digunakan untuk menjaga operasi sistem embedded tetap sinkron dengan clock. Clock dapat berupa clock eksternal atau clock sistem.
Timer digunakan untuk berbagai aplikasi dalam rangkaian atau sistem embedded seperti untuk menghasilkan baud rate, mengukur waktu-menghasilkan penundaan, dan banyak lagi. Timer sangat mudah diprogram daripada praktik pemrograman yang berbeda untuk iterasi loop. Timer menghitung siklus clock periferal atau dapat menghitung siklus clock dari clock yang dipasok secara eksternal. Pulsa clock juga dapat dihasilkan dengan bantuan timer yang juga disebut Baud Rate dari komunikasi serial.
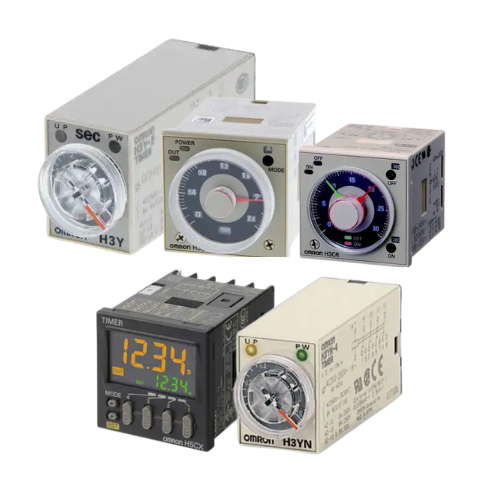


Jenis-jenis Timer
Dalam dunia otomasi dan pengendalian sistem, timer memiliki peran penting sebagai perangkat yang mengatur waktu operasi berbagai peralatan. Timer digunakan untuk mengatur durasi hidup atau mati perangkat secara otomatis, sehingga membantu meningkatkan efisiensi, keamanan, dan akurasi proses. Berdasarkan cara kerja, fungsi, dan aplikasinya, timer dapat diklasifikasikan ke dalam beberapa jenis, masing-masing dengan keunggulan dan karakteristik yang berbeda sesuai kebutuhan. Berikut adalah jenis-jenis timer yang umum digunakan dalam industri maupun aplikasi lainnya.
1. Timer Analog
- Timer analog menggunakan mekanisme berbasis dial atau knob untuk mengatur waktu operasi. Pengguna memutar dial ke posisi yang diinginkan untuk menetapkan durasi waktu tertentu. Timer ini dikenal karena kesederhanaannya dan kemudahan penggunaannya. Presisi relatif rendah karena bergantung pada akurasi mekanik potensiometer.
- Cara kerja timer analog: Mengatur waktu secara manual menggunakan knob putar, dengan waktu yang diatur melalui pergeseran mekanis.
- Aplikasi timer analog: Lampu otomatis sederhana dan Peralatan rumah tangga.
2. Timer Digital
- Timer digital adalah Timer yang menggunakan pengaturan berbasis layar digital dengan tombol atau keypad.
- Cara kerja timer digital: Mengatur waktu secara presisi melalui pengaturan digital dengan tampilan waktu di layar. Presisi tinggi karena waktu ditentukan secara elektronik dengan digital clock.
- Aplikasi timer digital: Kontrol sistem industri modern, Aplikasi HVAC, dan Sistem produksi otomatis.
3. Time Delay Relay (TDR)
- Time Delay Relay (TDR) adalah Komponen elektronik yang mengatur penundaan waktu untuk mengaktifkan atau mematikan relay.
- Cara kerja: Mengontrol waktu hidup/mati relay dengan menunda respons setelah sinyal input diterima. Presisi sedang, tergantung pada desain internal relay. Out put dapat mengontrol kontak NO atau NC pada relay untuk menghubungkan atau memutuskan rangkaian.
- Aplikasi: Otomasi industri (penundaan mesin) dan Sistem keamanan (penundaan alarm).
Fungsi Timer
1. Mengatur Waktu Operasi
Timer digunakan untuk memastikan bahwa suatu proses berjalan sesuai dengan durasi yang telah ditentukan, baik dalam hitungan detik, menit, hingga jam.
2. Menghemat Energi
Dengan timer, alat elektronik dapat dimatikan secara otomatis setelah digunakan, sehingga mengurangi pemborosan energi.
3. Meningkatkan Efisiensi
Timer membantu dalam meningkatkan efisiensi operasional di berbagai sektor, seperti produksi industri, sehingga mengurangi risiko keterlambatan.
4. Pengendalian Otomatis
Timer dapat diprogram untuk menjalankan tugas tertentu secara otomatis, seperti menyalakan lampu di waktu tertentu atau mengaktifkan mesin pabrik.
Mode Operasi Timer
Ada 4 mode operasi dasar pada timer, yaitu: Operasi ON-Delay, Operasi OFF-Delay, Operasi Flicker, Operasi Interval
Operasi ON-Delay
Pada mode operasi ini, timer mulai menghitung dan mengeluarkan output setelah interval waktu tertentu yang telah ditentukan. Timer ini disebut sebagai ON delay timer karena terdapat penundaan sebelum sinyal input diaktifkan. Mode operasi ON delay sering digunakan pada mesin otomatis.
Aplikasi: Sinyal Tombol Tekan (Pushbutton)
Ketika tombol tekan untuk pejalan kaki ditekan pada lampu lalu lintas, lampu sinyal berubah dari merah menjadi hijau setelah jeda waktu tertentu.
Operasi OFF-Delay
Dalam mode OFF delay, timer mulai bekerja segera setelah input diaktifkan. Output timer juga dimulai bersamaan, tetapi output akan berhenti setelah waktu yang telah ditentukan habis. Waktu ini dihitung sejak input dimatikan. Contoh dasar dari OFF delay timer adalah lampu indikator pintu pada mobil.
Aplikasi: Lampu Plafon Mobil
Saat Anda masuk ke dalam mobil, lampu plafon menyala ketika pintu dibuka. Lampu akan tetap menyala selama beberapa detik setelah Anda masuk ke dalam mobil dan menutup pintu.
Operasi Flicker
Pada mode operasi flicker, output akan secara berulang menyala dan mati pada waktu yang telah ditentukan setelah menerima input.
Aplikasi: Pengendalian Otomatis Air Mancur
Air mancur secara berulang akan menyemprotkan air dan berhenti dengan interval waktu dua menit.
Operasi Interval
Pada mode operasi interval, timer mengeluarkan output untuk jangka waktu tertentu setelah input diterima.
Aplikasi: Wahana di Taman Hiburan
Wahana akan beroperasi selama lima menit setelah koin dimasukkan.


Contract management
E-procurement includes tools for managing contracts electronically, from creation and negotiation to execution and renewal. This function ensures contractual terms and conditions compliance, reduces risks and improves contract lifecycle management.


Invoicing and payment
The system automates the processing of invoices, matching them with purchase orders and delivery receipts to ensure accuracy before payment. This reduces the risk of errors, prevents fraudulent activities, and accelerates the payment process.

Reporting and analytics
Provide advanced reporting and analytics tools, offering insights into spending patterns, and supplier performance. These insights help organizations make informed decisions, identify cost-saving opportunities, and optimize their procurement strategies.
3. What is the e-procurement process?
The e-procurement process typically follows these key stages:
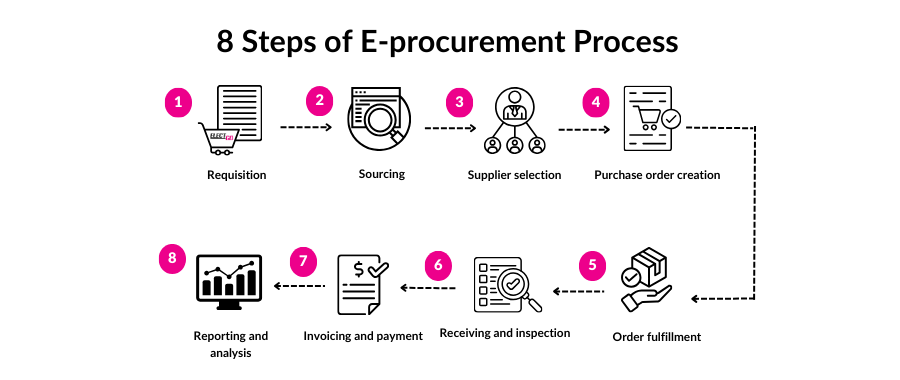
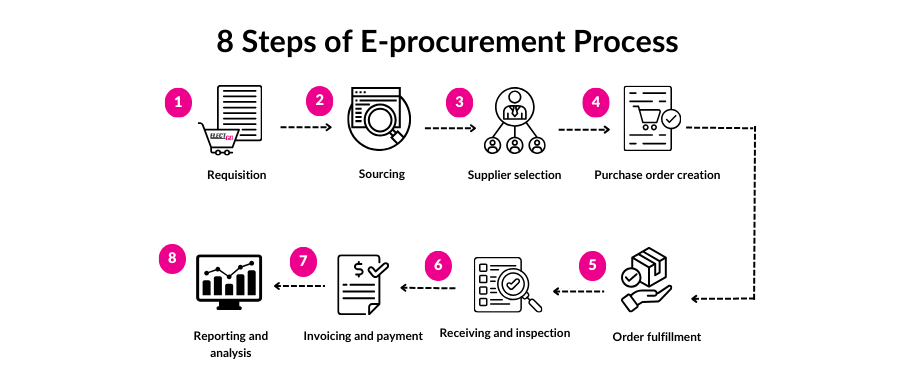
3.1 Requisition
The process begins with the submission of a purchase requisition by a department or employee, which outlines the required goods or services. The e-procurement system routes this requisition through an automated approval workflow based on pre-established rules.
3.2 Sourcing
Once the requisition is approved, the e-procurement system facilitates the sourcing process. This may involve sending out requests for proposals (RFPs) or quotes (RFQs) to prequalified suppliers, hosting online auctions, or accessing digital catalogs to find the best suppliers.
3.3 Supplier selection
Suppliers submit their bids or quotes electronically, which are then evaluated by the procurement team. The e-procurement system helps compare bids based on criteria such as price, delivery time, quality, and compliance with specifications. The selected supplier is then notified electronically.
3.4 Purchase order creation
After the supplier is chosen, the e-procurement system automatically generates a purchase order (PO) based on the requisition and supplier information. This PO is sent to the supplier electronically, confirming the order details.
3.5 Order fulfillment
The supplier fulfills the order by delivering the goods or services as specified. The e-procurement system tracks the order status, ensuring timely delivery and notifying the buyer of any delays or issues.
3.6 Receiving and inspection
Upon receiving the goods or services, the buyer inspects them to ensure they meet the specified requirements. The e-procurement system records the receipt and any discrepancies, if any, in the delivery.
3.7 Invoicing and payment
The supplier submits an electronic invoice, which is matched with the purchase order and receipt in the e-procurement system. Once verified, the payment is processed automatically, completing the transaction.
3.8 Reporting and analysis
The e-procurement system captures data throughout the process, generating reports and analytics to provide insights into procurement activities. This data can be used to evaluate supplier performance, identify savings opportunities, and improve future procurement strategies.
4. What are the benefits and drawbacks of e-procurement?


4.1 Benefits of e-procurement
- Increased efficiency: By automating routine tasks such as order processing, approval workflows, and invoicing, eProcurement reduces the time and effort required to complete procurement activities, allowing procurement professionals to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Cost savings: Achieve better pricing through competitive bidding, bulk purchasing, and improved supplier negotiations. It also reduces administrative costs by minimizing manual processes and errors.
- Enhanced transparency: Provide real-time visibility into procurement activities, ensuring compliance with procurement policies and reducing the risk of fraud. Audit trails and reporting features also enhance transparency and accountability.
- Better supplier management: Improve supplier relationships by providing tools for performance monitoring, communication, and collaboration. Suppliers benefit from streamlined processes, faster payments, and increased business opportunities.
- Improved compliance: Ensures that all procurement activities adhere to organizational policies and regulatory requirements. Automated approval workflows and contract management tools help enforce compliance and reduce risks.
- Data-driven decision-making: Provide valuable insights into procurement activities through advanced reporting and analytics tools. Organizations can use this data to optimize procurement strategies, identify cost-saving opportunities, and improve supplier performance.
4.2 Drawbacks of e-procurement
- Implementation costs: Can be expensive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Costs may include software licensing, customization, training, and integration with existing systems.
- Complexity: Can be complex to implement and operate, requiring significant changes to existing procurement processes. Organizations may need training and change management to ensure successful adoption.
- Dependence on technology: E-procurement system relies heavily on technology, making it vulnerable to system downtime, cybersecurity threats, and data breaches. Organizations must ensure their eProcurement systems are secure, reliable, and regularly updated.
- Resistance to change: Employees and suppliers may only accept transitioning from traditional procurement methods to e-procurement, especially if unfamiliar with the new technology. This resistance can hinder the system’s successful adoption.
5. What are the differences between e-procurement and procurement
| Factor | E-procurement | Procurement |
| Sourcing and acquiring goods/services | Digitally enhances this process by integrating technology to streamline and automate the procurement activities. | Involves sourcing, negotiating, and acquiring goods, services, or works from external suppliers. |
| Supplier management | Digitizes supplier management tasks such as supplier bidding and selection through automated systems. | Includes activities like supplier selection and contract management. |
| Order processing | Automates order processing tasks like purchase requisitions and invoice processing, reducing manual effort and errors. | Involves order processing, which is typically done manually or through paper-based methods. |
| Efficiency and transparency | Enhances efficiency, transparency, and data-driven decision-making by leveraging digital tools and real-time insights. | Aimed at managing the procurement process, though it may be time-consuming and prone to errors due to manual processes. |
6. What are the common e-procurement solutions in the market?
The e-procurement market offers a variety of solutions, each designed to address specific procurement challenges and requirements. Some common e-procurement solutions include:
- Credit term solution provides a mechanism for managing financial transactions between buyers and suppliers, offering flexibility in payment and improving cash flow. It also enhances procurement efficiency and financial management, making them a valuable component of a comprehensive eProcurement strategy
- Punchout solution is a digital catalogs that allow buyers to browse and purchase goods and services from pre-approved suppliers. eCatalogs streamline the purchasing process, ensuring compliance with procurement policies and reducing maverick spending.
- Supplier portals: Online platforms that facilitate communication and collaboration between buyers and suppliers. Supplier portals provide a centralized hub for managing interactions, streamlining procurement processes, and exchanging information. Through these portals, suppliers can submit bids, manage orders, track payment status, and access important documents and updates. Buyers, in turn, can review supplier performance, manage contracts, and ensure compliance with procurement policies.


Additional e-procurement solution resources
Interested in knowing more about e-procurement solutions? Check out these available resources on ElectGo.
Share this article on social media